- INTRODUCTION
- Course Objectives:
- COMPUTER BASICS
- SAFE ONLINE RESEARCH
- Research on the Web:
- Using Social Media:
- USING GOOGLE & BING
- Using Google Search:
- Using Bing's AI Function:
- STEPS OF CREATING CAMPAIGN
- PROTECTION AGAINST OCSE USING GOOGLE RESEARCH
- PROTECTION AGAINST OCSE USING BING'S AI FUNCTION
- Home Assignment
INTRODUCTION #
An introduction to a computer literacy course typically provides students with fundamental knowledge and skills needed to navigate and utilize computer technology effectively. Here’s an overview of what such a course might cover:
Course Objectives: #
The primary goals of an introduction to computer literacy course are to:
1. Familiarize Students with Computer Basics:
Ensure that students understand the fundamental components of a computer system, including hardware and software.
2. Teach Basic Computer Operations:
Cover essential skills such as turning the computer on/off, using input devices (keyboard and mouse), and navigating the operating system.
3. Introduce Software Applications:
Provide an overview of commonly used software applications, such as word processors, spreadsheets, and web browsers.
4. Promote Digital Communication:
Students will learn how to use email and other communication tools, emphasizing netiquette and online safety.
5. Develop Internet Skills:
Introduce web browsing, online research, and the responsible use of online resources.
6. File Management:
Students will learn how to create, organize, and manage files and folders on their computer.
7. Basic Troubleshooting:
Equip students with problem-solving skills for common computer issues, such as resolving software errors and hardware connectivity problems.
8. Introduce Cybersecurity Awareness:
Raise awareness about online safety, the importance of strong passwords, and recognizing common online threats like phishing.
– Recognizing and avoiding online threats (phishing, malware).
COMPUTER BASICS #
1. Switching on the computer:
– Locate the computer’s power button. It’s usually located on the front or side of a desktop computer and on the top or side of a laptop. It’s in a different place on every computer, but it will have the universal power button symbol. Once turned on, your computer takes time before it’s ready to use. You may see a few different displays flash on the screen. This process is called booting up, and it can take anywhere from 15 seconds to several minutes.
2. Logging In:
– After the computer boots up, it can be immediately usable or it might ask you to log in. This entails entering your user’s name or choosing your profile before entering your password to prove who you are. You might need to create an account if you’ve never logged in to your computer before.
If the computer has multiple user accounts, you may need to select your user profile and enter your password or PIN to access the desktop.
– If it’s a new computer, you could require to go through an initial setup process, including creating a user account and setting a password.
3. Using the Desktop:
– Once you’re logged in, you’ll see the desktop. This is your main workspace. This is sort of like a main menu or a table of contents. From here, you can access the programs and features you need to use your computer.
Icons while using desktop represent files, folders, and applications. You can double-click on them to open or launch them.
4. Using the Start Menu (Windows) or Dock (macOS):
– In Windows, click the “Start” button in the lower-left corner to access the Start Menu. Here, you can find and open applications, access settings, and search for files.
– In macOS, the Dock at the bottom of the screen contains frequently used apps. You can click on these icons to open them.
5. Connecting Accessories:
– If you have accessories such as a keyboard, mouse, printer, or external hard drive, connect them to the computer’s available ports (USB, HDMI, etc.).
– Most accessories are plug-and-play, which means they should work automatically. If not, you may need to install drivers provided by the manufacturer.
6. Saving Documents:
– When you create or edit a document, you’ll want to save it. In most applications, you can go to “File” and then “Save” or “Save As.”
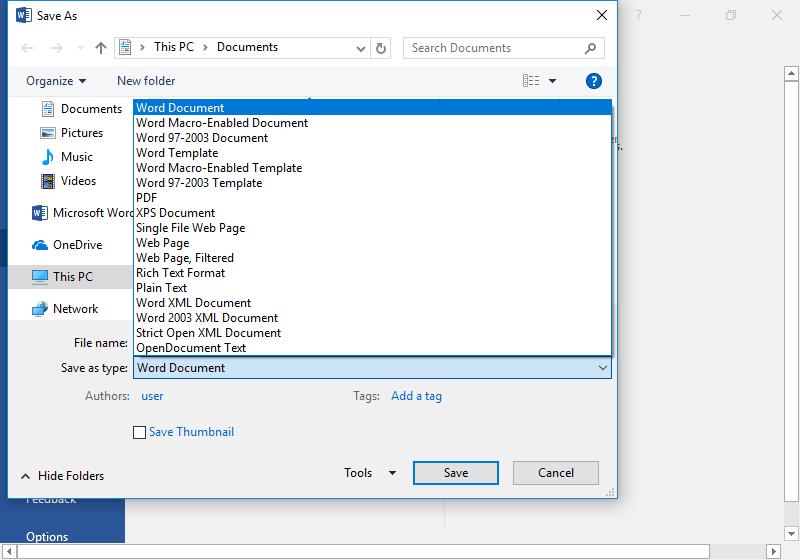
– Choose a location on your computer to save the file, such as the Documents folder.
– Give the file a name and choose a file format (e.g., .docx for Word documents or .jpg for images).
7. Organizing Files and Folders:
– It’s a good practice to organize your files into folders. To create a new folder, right-click on the desktop or in a file explorer window, select “New,” and then “Folder.”
– Name the folder and drag and drop files into it for organization.
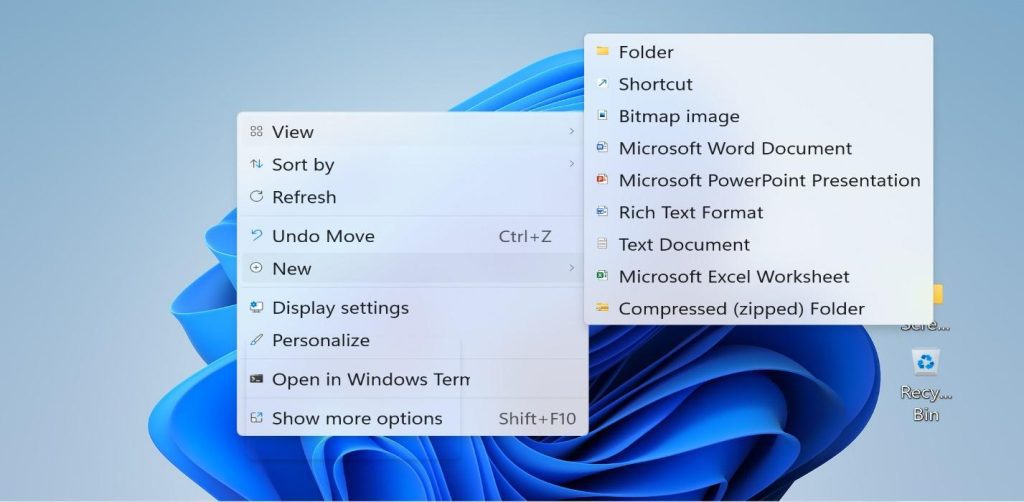
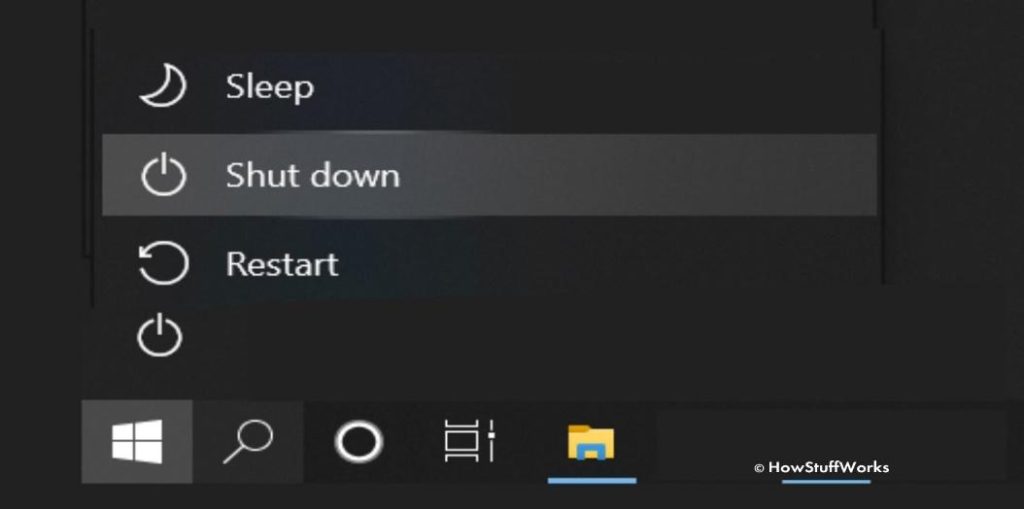
8. Shutting Down the Computer:
– When you’re done using the computer, you can shut it down. In Windows, click the “Start” button, then the power icon, and select “Shut Down.” In macOS, go to the Apple menu and choose “Shut Down.”
Remember, learning to use a computer takes time and practice so, be patient and do enough practice to reach the mastery level.
SAFE ONLINE RESEARCH #
Being safe online is crucial when conducting research on the web and using social media platforms. Here are some important tips to ensure your online safety in these contexts:
Research on the Web: #
1. Use Reliable Sources:
– Stick to reputable websites, academic journals, and government websites for research. Be cautious of sources with suspicious or biased information.
2. Check Website Security:
– Ensure the websites you visit for research use secure connections (look for “https://” in the URL) and have a trustworthy reputation.
3. Verify Information:
– Cross-check facts and information from multiple sources to verify their accuracy before citing or sharing them.
4. Beware of Phishing Scams:
– Be cautious of unsolicited emails or links that ask for personal information or login credentials. Verify the sender’s identity before responding or clicking on links.
5. Use Strong Passwords:
– Create unique, strong passwords for your online accounts, especially if you need to log in to access research materials or databases.
6. Update Software and Antivirus:
– Keep your computer’s operating system, web browsers, and antivirus software up to date to protect against security vulnerabilities.
7. Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Research:
– Public Wi-Fi networks can be insecure. If possible, use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) or a secure network when accessing sensitive research materials.
8. Clear Browser Cookies and History:
– Regularly clear your browsing history and cookies to reduce the chances of advertisers tracking your online activity.
9. Use Ad-Blockers and Privacy Plugins:
– Consider using browser extensions that block ads and enhance privacy to reduce tracking and potential security risks.
Using Social Media: #
1. Adjust Privacy Settings:
– Review and customize your privacy settings on social media platforms to control who can see your posts, personal information, and contact you.
2. Be Cautious with Personal Information:
– Avoid sharing sensitive personal information, such as your full address, phone number, and financial details, on social media.
3. Think Before You Post:
– Be mindful of the content you share. Once something is online, it can be challenging to remove completely.
4. Beware of Friend Requests and Messages:
– Be cautious when accepting friend requests or messages from people you don’t know. Verify the identity of new contacts before engaging with them.
5. Recognize Fake Profiles and Scams:
– Watch out for fake profiles and phishing attempts. If something seems suspicious, report it to the platform administrators.
6. Use Strong, Unique Passwords:
– Employ strong, unique passwords for your social media accounts and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) if available.
7. Regularly Review and Clean Up Your Friends/Followers:
– Periodically review your friends or followers list and remove any accounts that you no longer recognize or trust.
8. Educate Yourself on Privacy Features:
– Familiarize yourself with the platform’s privacy features and settings to better protect your information.
9. Avoid Oversharing:
– Refrain from sharing excessively personal or intimate details of your life online, as this information can be misused.
By following these guidelines, you can enhance your online safety while conducting research and using social media. It’s essential to stay informed about potential risks and take proactive steps to protect your digital presence.
USING GOOGLE & BING #
Certainly, you can use both Google and Bing to research and learn about online safety and how to protect yourself against online child sexual exploitation (OCSE). Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to utilize these search engines effectively:
Using Google Search: #
1. Open Your Web Browser:
– Launch your preferred web browser (e.g., Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari).
2. Go to Google:
– Type “www.google.com” in the browser’s address bar and press Enter.
3. Enter Your Query:
– In the Google search bar, enter your query. For example, you can start with a general query like “online safety tips” or “protecting against OCSE.”
4. Use Specific Keywords:
– To get more relevant results, use specific keywords in your query, such as “child online safety guidelines” or “how to report online child exploitation.”
5. Review Search Results:
– Google will display a list of search results. Click on the most relevant links to learn about online safety and OCSE prevention.
6. Explore Reputable Sources:
– Look for results from reputable sources like government websites, non-profit organizations, and educational institutions. These sources often provide reliable information.
7. Check Date and Credibility:
– When reading articles or guides, check for the publication date to ensure the information is current and relevant. Verify the credibility of the source.
8. Use Google Images and Videos:
– If you’re looking for visual content or resources, you can use Google Images and Google Videos to find relevant multimedia.
Using Bing’s AI Function: #
Bing offers an AI-powered feature called “Intelligent Answers” that can help you find information more efficiently. Here’s how to use it:
1. Go to Bing:
– In your web browser, visit the Bing search engine by typing “www.bing.com” in the address bar and pressing Enter.
2. Enter Your Query:
– In the Bing search bar, enter your query related to online safety or OCSE prevention.
3. Explore Intelligent Answers:
– Bing will often display “Intelligent Answers” at the top of the search results. These are concise, informative responses to common questions. Click on them for quick insights.
4. Review Standard Search Results:
– Below the Intelligent Answers, you’ll see the standard search results. Click on relevant links to access more in-depth information.
5. Use Filters:
– Bing also provides filters on the left side of the search results page. You can use these filters to refine your search by type (e.g., web pages, images, videos) or date.
6. Explore Visual Results:
– Bing often includes visual content, such as images and videos, in its search results. Click on these elements to access multimedia resources.
7. Verify Sources:
– As with Google, verify the credibility of the sources you consult for information on online safety and OCSE prevention.
Remember to take your time when researching this sensitive topic and ensure you are accessing information from reputable sources. Additionally, consider using multiple search queries to gather a well-rounded understanding of online safety and how to protect against OCSE.
Certainly, you can use search engines like Google and Bing to gather information on how to protect yourself and others against online child sexual exploitation. Here’s how you can approach your research using both search engines:
STEPS OF CREATING CAMPAIGN #
Creating an online campaign can be a powerful way to raise awareness, promote a cause, or advocate for change. Here are the steps to create campaign a campaign AGAINST ONLINE CHILD SEXUAL EXPLOIATATION:
1. Define Your Goal and Purpose:
– Clearly articulate the objective of your campaign. What do you want to achieve?
– Identify your target audience, as this will influence your messaging and strategy.
2. Research and Planning:
– Research the issue or cause you’re advocating for. Understand the facts, statistics, and key points.
– Study successful campaigns related to your cause to learn from their strategies.
– Develop a campaign plan, including a timeline, budget (if applicable), and key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure success.
3. Create a Compelling Message:
– Craft a clear and compelling message that resonates with your target audience.
– Use persuasive language and storytelling techniques to evoke emotions and engagement.
– Make your message concise and easy to understand.
4. Choose the Right Platforms:
– Identify the online platforms and channels where your target audience is most active.
– Consider using social media (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, Instagram), email newsletters, a campaign website, or other digital tools.
5. Develop Content:
– Create content that supports your message, including text, images, videos, and infographics.
– Ensure your content is visually appealing and shareable.
6. Engage Your Audience:
– Use social media and other communication channels to engage with your audience.
– Respond to comments and messages promptly.
– Encourage user-generated content, such as user testimonials and stories.
7. Leverage Influencers and Partners:
– Collaborate with influencers or organizations that align with your cause to expand your reach.
– Partner with relevant stakeholders who can amplify your message.
8. Launch Your Campaign:
– Set a launch date and time to create a sense of urgency.
– Coordinate your messaging across all platforms for a unified campaign launch.
9. Measure and Analyze:
– Track the performance of your campaign using key performance indicators (KPIs) defined in your plan.
– Analyze data to see what’s working and what needs improvement.
– Adjust your strategy as needed during the campaign
10. Engage in Outreach and Advocacy:
– Reach out to media outlets, bloggers, and influencers to secure coverage and support.
– Encourage your supporters to take action, such as signing petitions, sharing content, or making donations.
11. Sustain Momentum:
– Keep the momentum going beyond the initial launch by continuing to share updates and engage with your audience.
– Consider hosting events or webinars related to your cause.
12. Evaluate and Report:
– After the campaign ends, evaluate its overall success against your goals.
– Prepare a report summarizing the impact of your campaign and share it with your supporters and stakeholders.
Remember that creating a successful online campaign may take time, effort and basic computer knowledge. It’s important to stay ethical, transparent, and compliant with the rules and policies of the platforms you use. Additionally, be prepared to adapt your strategy based on the feedback and results you receive during the campaign.
PROTECTION AGAINST OCSE USING GOOGLE RESEARCH #
Using Google:
a. Open your web browser and go to the Google homepage.
b. In the search bar, enter relevant keywords or phrases, such as:
– “How to protect against online child sexual exploitation”
– “Online safety tips for children”
– “Internet safety guidelines for parents”
c. Browse through the search results. Look for credible sources such as government websites, non-profit organizations, and educational institutions. These sources often provide reliable information and guidelines.
d. Click on the search results that seem informative and relevant to your topic. Pay attention to articles, guides, and resources that offer practical advice on online safety.
e. Take notes or bookmark useful pages for future reference.
PROTECTION AGAINST OCSE USING BING’S AI FUNCTION #
Using Bing’s AI Function:
a. Go to the Bing search engine.
b. In the search bar, enter a similar set of keywords or phrases related to online child sexual exploitation protection.
c. Browse through the search results and take note of any featured snippets or information provided directly by Bing’s AI.
d. Click on the results that seem promising for more detailed information.
e. Consider using Bing’s intelligent search features to narrow down your results. For example, you can use Bing’s image and video search features to find visual resources related to online safety.
Remember to evaluate the credibility of the sources you encounter during your research. Government websites, reputable organizations, and educational institutions are often reliable sources for information on online child safety. Additionally, consider exploring resources specifically tailored to parents, caregivers, and children to better understand the best practices for online safety and protection against child exploitation.
Home Assignment #
Use your phone to continue research about OCSE. (1 Hour)



